Warts are non-cancerous skin growths caused by certain strains of the human papillomavirus (HPV). They can appear anywhere on the body, commonly on the hands, feet, and genitals. Although often harmless, they can be unsightly and uncomfortable, particularly if left untreated.
Types of Warts
- Common Warts: Typically found on the hands and fingers, these warts have a rough, raised appearance.
- Plantar Warts: Develop on the soles of the feet, often causing pain due to pressure while walking. Unlike other warts, plantar warts grow inward because of this pressure.
- Flat Warts: Smaller and smoother than other types, flat warts often appear in clusters, especially on the face, hands, or legs.
- Genital Warts: A sexually transmitted type of wart that appears on or near the genitals and can lead to discomfort, itching, or pain.
Causes and Spread
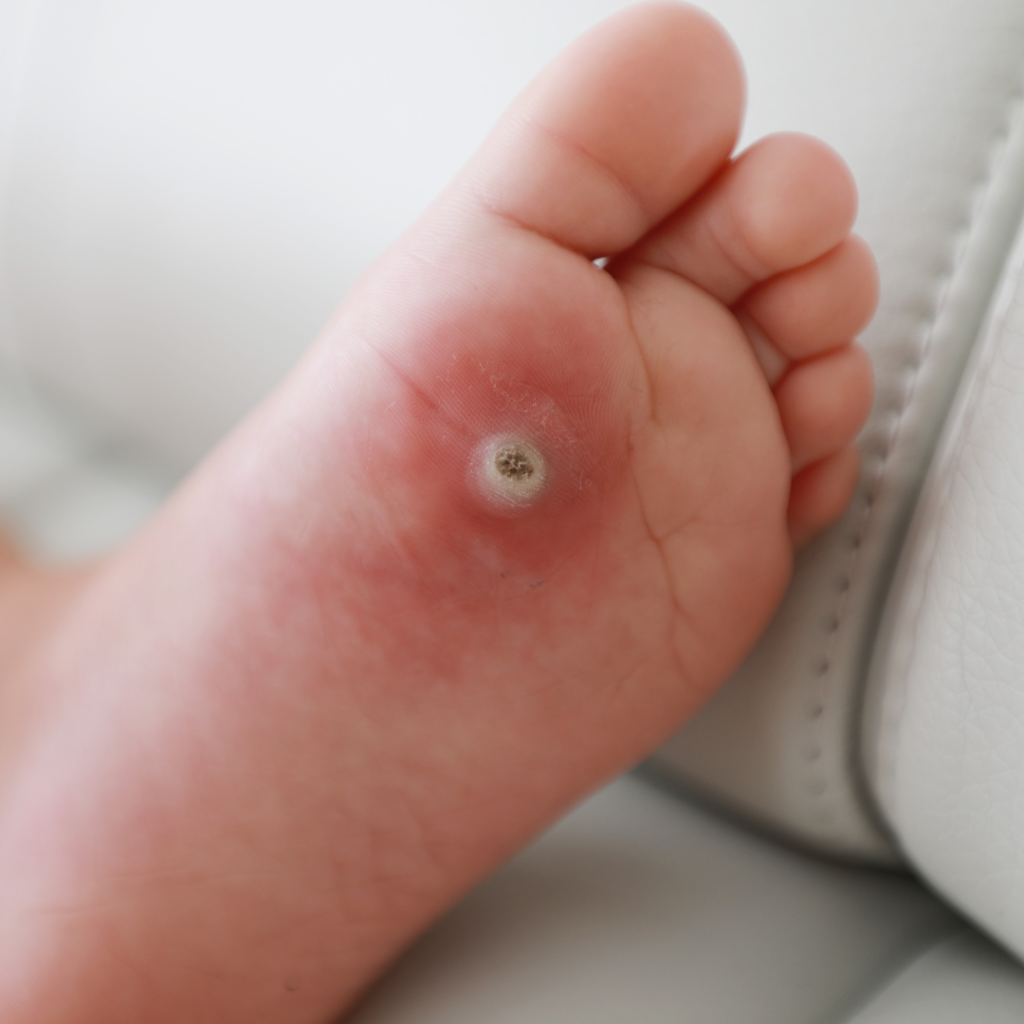
Warts are caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV), which enters the body through small cuts or abrasions in the skin. Once infected, the virus triggers rapid cell growth, resulting in a wart. HPV spreads through skin-to-skin contact and contaminated surfaces, making contagious skin warts a concern for those in close physical contact with an infected person.
Certain risk factors can increase the likelihood of developing warts:
- Weak immune system: Individuals with weakened immune systems are more susceptible to the virus.
- Skin damage: Open wounds or scratches provide easy entry for HPV.
- Moist environments: Warm, moist conditions, such as swimming pools and locker rooms, can promote wart transmission.
Prevention Tips
While there’s no surefire way to prevent warts entirely, there are steps you can take to reduce your risk:
- Avoid direct contact with warts, whether on yourself or others.
- Keep cuts and abrasions clean and covered to prevent HPV entry.
- Wear flip-flops or sandals in communal areas like locker rooms and pools to avoid plantar warts.
- Practice safe sex to reduce the risk of genital wart transmission.
- Boost your immune system through a healthy diet and lifestyle.
Treatment Options
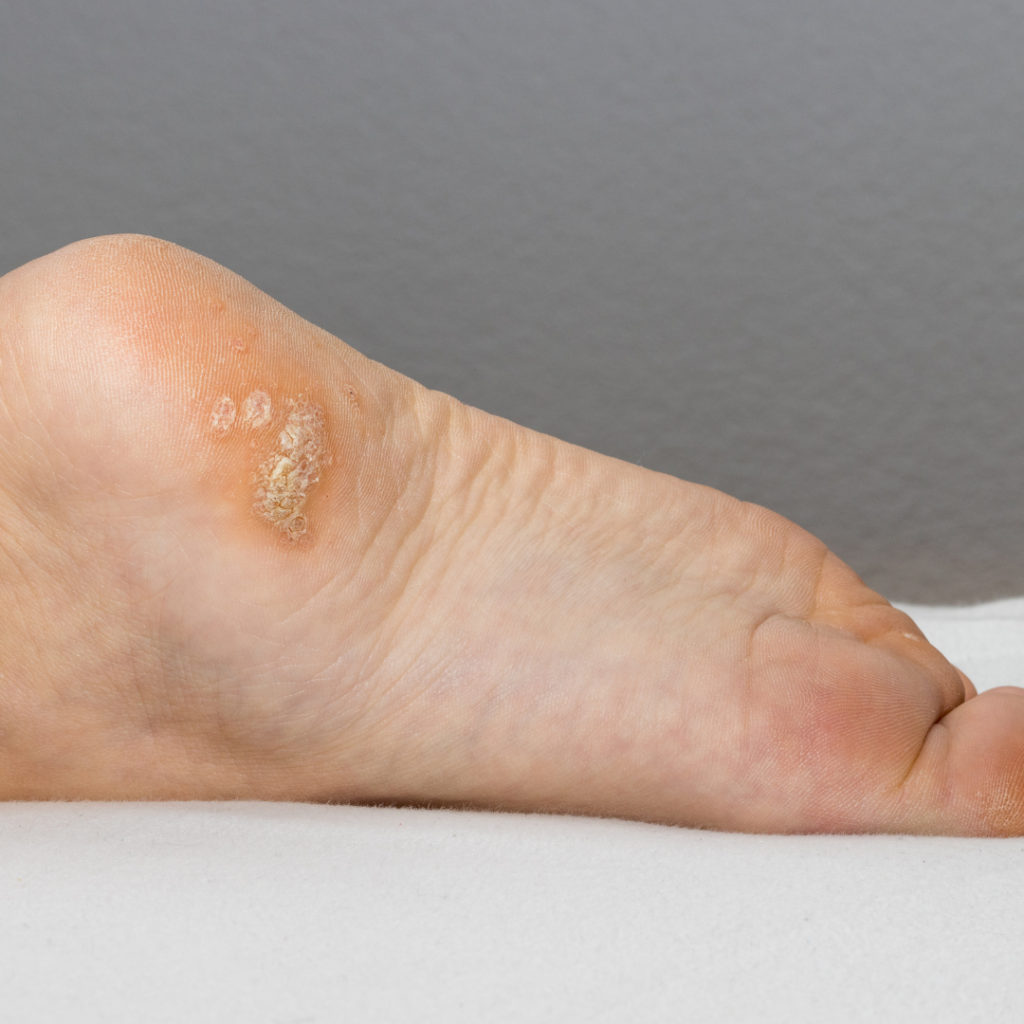
Although warts may disappear on their own, many choose to remove them due to pain, discomfort, or aesthetic reasons. Various treatments are available depending on the type of wart and its location.
- Cryotherapy for Warts
This common method involves freezing the wart with liquid nitrogen. The cold causes a blister to form around the wart, which eventually falls off after a week or so. Cryotherapy can be effective but may require multiple treatments for stubborn warts. - Plantar Wart Removal
Plantar warts can be particularly challenging to treat because they grow inward. Treatments like salicylic acid, a topical treatment that peels away the infected skin, are often used. For more severe cases, cryotherapy or laser treatments may be necessary. - Laser Wart Removal
Laser treatment is typically reserved for warts that do not respond to other treatments. The laser destroys the blood vessels feeding the wart, causing it to die and fall off. This procedure can be especially helpful for genital warts or flat warts that persist despite other treatments. - Genital Wart Treatment
Genital warts require special care due to their sensitive location. Prescription creams and ointments, such as imiquimod, can stimulate the immune system to fight the virus. In more severe cases, cryotherapy, laser therapy, or surgical removal may be required. Consult with a healthcare provider for the best course of action.
HPV Wart Prevention
While warts themselves are not always preventable, the HPV vaccine can significantly reduce the risk of certain types of warts, particularly genital warts and those associated with cancers. The vaccine is recommended for preteens but can be administered to adults who have not yet been vaccinated. Practicing safe sex and maintaining proper hygiene are also important steps in preventing the spread of HPV-related warts.
When to See a Doctor
Most warts are harmless and can be treated at home using over-the-counter remedies like salicylic acid or freezing kits. However, you should see a healthcare provider if:
- The wart changes in color or shape.
- The wart is painful or bleeds.
- Over-the-counter treatments are ineffective.
- You have warts on sensitive areas like the face or genitals.
- You have a weakened immune system and are prone to infections.
Consulting a professional ensures that you receive the appropriate treatment, particularly if the wart is persistent, painful, or in an uncomfortable location. A doctor may recommend more aggressive treatments like laser therapy, cryotherapy, or surgical excision to fully remove the wart.
Conclusion
Warts, though common and usually harmless, can be bothersome both physically and aesthetically. Whether you’re dealing with plantar warts, genital wart treatment, or persistent flat wart causes, knowing the available options and preventive measures is key to effective management. For stubborn or painful warts, professional treatments like cryotherapy or laser wart removal can offer relief and restore comfort and confidence.
By staying vigilant about hygiene and seeking timely treatment, you can reduce your risk of warts and limit their spread.
For a Radiance solution, book a consultation.

Leave a Reply